We recently announced a strategic joint venture with Google Cloud, which integrates Plataine’s AI software with Google Glass and Google’s Dialogflow Enterprise Edition for native language processing.
You can review Plataine’s offering regarding Google Smart Glasses here.
Since our announcement, multiple partners, customers, industry pros and colleagues have asked us about this partnership in an attempt to better understand the innovation and opportunity it presents to manufacturers. In other words, we realized that manufacturers want to see some concrete use cases and understand where this is going to.
Therefore I’ve decided to share our perspective.
IIoT, along with AI capabilities, has completely transformed modern manufacturing, from the way information is processed to how factory workers operate to the amount of tasks they can manage.
But along with this change, new challenges were born. The flow of endless information enforces site managers and workers to stay aligned and, more than ever before, remain quick and accurate in their work. IIoT enabled manufacturers to achieve much bigger production scales (get this white-paper on how IIoT can help you boost production speed and lower costs), but this led to an increase in the number of instant decisions they have to make.
New opportunities are born. Real challenges were born as well.
How should factory workers solve such complexities? How can they analyse multiple and sometimes critical data in a transparent and seamless way throughout their entire work day?
Since you know the ropes, you already know that factory floor workers can’t stay connected to their laptops or tablets. They have to go between workstations, stop by machinery, visit production lines, while in some cases several users share one desktop.
In order for factory workers to be able to handle a huge amount of information, and deal with its various complexities, there’s a need for a special human ‘personal assistant’ that would follow them everywhere they go on the floor, providing them with insights and recommendations in real time without interrupting and slowing workers down.
As far as I know, there’s only one pair of hands and one brain per human.
That’s ok, as leveraging technology can help. Technology can assist factory workers in accessing needed data, right when they need it, while keeping their hands free and while being away from their laptops.
Yes, you guessed right. That’s where smart glasses, such as Google’s new Glass Enterprise Edition, come in.
Smart Glasses and Industrial Manufacturing
Since Google Glasses were first introduced in 2013, a lot has changed.
Though smart glasses didn’t take off in the consumer market, partly due to privacy and security concerns, (in January 2015 Google even stopped selling glasses to the general public), the implementation of smart glasses for the needs of enterprises seems to be right on the money.
You know that old saying: ‘Where there’s a need, there’s a way’? Well, I can only guess that the pain points that I described above paved (and still pave) the way to a very valuable connection between industrial IoT and wearables.
Take IIoT, add AR and use wearables such as smart glasses, and you’re closer to an extra brain as well as freeing up employees’ working hands. That’s how you harness smart glasses at the service of enterprises in general, and manufacturing specifically.
Predictions are optimistic and coincide with the positive connection between wearbles and manufacturing:
- Back in 2013, Gartner predicted that ‘Smart glasses are expected to have the most impact on the heavy industry, such as manufacturing…’
- According to Zebra Technologies more than half of manufacturers surveyed expressed a desire to adopt wearable technology by 2022. Of those currently using wearables, 55% said they plan to increase their usage.
- According to Taptica, 75 million wearable devices are to be deployed in enterprise and industrial environments by 2020.
- Forrester predicts that more than 14 million U.S. workers will use smart glasses by 2025.
- Forrester also predicts that enterprises are expected to spend more than $30 billion on smart glasses through 2025.
Why are these predictions so high? Well, it all boils down to the benefits:
Productivity
When I think of productivity in this aspect, I like to divide it to 2 main areas:
- Real-time data, alerts and recommendations that support fast and optimal decision making. This also includes automation of tracking and reporting (according to CIOs that we’ve interviewed, 20% of workers time is wasted on reporting).
- Freeing workers hands (no need to explain why this boosts efficiency)
Smart glasses can seamlessly provide workers with valuable insights, alerts and recommendations on the go, in real-time and in exact context, saving them precious time and effort. The ability to natively talk and preform production activities while seeing complementary information will reduce distractions and keep the operator focused on getting the job done right.
For instance, employees can locate and physically find products or tools easily by receiving exact visual directions while walking the production floor (think of in-door navigation with the help of image recognition algorithms and video capabilities). A known related use case is DHL, but we’ll get to them later on.
In respect to manufacturing environment maintenance, starting from the equipment and machinery, to different production stages, to the completed product and even to the supply chain management, technicians can view the status of items, log inspection results and more, all through wearable smart glasses. There’s no longer the need to go back to their office desk and turn on their laptop or find their tablet.
For production floor workers that’s a game changer.
Real time access to valuable information also allows factory workers to quickly adjust work processes if needed, as well as to not be delayed when urgent alerts pop up, making them much more efficient. Using video capabilities, one of the smart glasses known benefits, workers can also share exactly what they see with remote experts and hence make better decisions.
Safety
Factory worker safety and the physical risks that are involved in manufacturing continue to be burning issues that wearables are attempting to improve. Smart glasses, obviously, allow a hands free operation which improves worker safety.
Employee training and troubleshooting
One of the interesting implications of smart glasses in manufacturing relates to the ability to train employees. In the Gartner prediction (that smart glasses will have the highest impact on heavy industries), there’s a demonstration of some of the benefits as it relates to employee training: ‘AR glasses enable on-the-job training of workers in how to fix equipment and perform manufacturing tasks.’
Here’s another related benefit – Using the glasses, new employees can experience complete, simulated training or a training can be recorded by experienced employees.The glasses can offer possible solutions to problems and even connect the user with experts who that can watch exactly what the employee sees through the glasses and provide remote assistance. The later is also relevant to experienced employees that require expert advise and troubleshooting.
Since learning never ends, in the near future smart glasses will be able monitor employee actions and produce smart analysis. For instance the glasses can determine if the employee takes longer to do a certain step than recommended which could lead to further training of staff members.
Quality
Smart glasses also support quality improvements. Incorrect and delayed reporting might cause quality issues, Automating the reporting process and doing it in real time dramatically improves quality. Predictive alerts, actionable insights and optimized recommendations that empower production staff to make better decisions increase overall quality of processes as well. For instance, image recognition algorithms combined with IIoT’s AI algorithms can allow an automatic identification of production defects or problems early on, or they can predict them even before they occur, ensuring on-time, on-quality delivery.
Even quality assurance processes can be improved by allowing workers to compare photos (taken with smart glasses) of inspected parts or assembly processes. They can then compare the images to vetted part images using their smart glasses. Defects will be pointed out via the glasses, helping technicians to work more efficiently.
Big names are already on-board
Some known manufacturing companies have already started leveraging smart glasses:
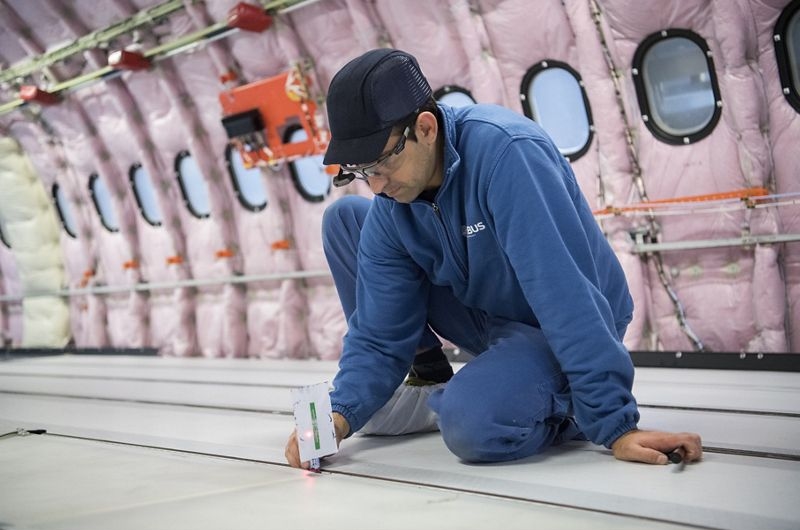
‘Airbus “sees the future through the vision of smart glasses”.’ Airbus uses smart glasses to enable greater efficiency and time saving during the outfitting of Airbus aircrafts. Cédric Gardon, the Industrialization Technical Manager for Flight Test Installation is quoted, saying: ‘Before the arrival of smart glasses for in-cabin applications, we had to decipher complex drawings and convert imperial measurements into metric measurements in marking the position of the equipment on the cabin floor’. In plain English, they had to apply a very accurate, to the millimeter, positioning in the process of the cabin installation marking. ‘We were surprised at how much time we saved,’ he said. ‘The operation used to require three people and three days; now it requires one single operator and six hours.’
GE uses smart glasses to help workers assemble wind turbines, allowing them easy access to directions and training them in their line of sight. In addition to data layers, workers can view videos or voice commands and interact with experts for further remote real time assistance and troubleshooting. GE reports ‘a 34% improvement in productivity the very first time the technician used the wearables, versus operating the standard way.’
AGCO offer another interesting use case to look at. Agco implemented smart glasses to assist in quality control and train new employees by breaking down common tasks into mini steps, and they used voice command to allow the employees to ask for further information. Peggy Gulick, AGCO’s Director of Business Process Improvement, said, ‘We have discovered that training with smart glasses is a grand slam. New product launches, multi-operation and new hire training are easily administered and audited for success.’ As for the numbers, AGCO report a ‘30% reduction in inspection time, with the elimination of paperwork and manual uploading, a 25% reduction in production time on low volume, complex assemblies and an impressive 50% learning curve reduction for new hires!’
DHL is using smart glasses in warehouses in DHL’s supply chain to help workers receive instructions on where items should be placed, including visual assistance. DHL managed to show ‘an average improvement of productivity by 15% and higher accuracy rates.’
Summary
It is only fitting that smart factories will pair up with smart glasses to create a smarter, advanced industrial environment. When you are in the process of selecting your prefered IIoT solutions don’t hesitate to also ask about smart glasses integrations – it could save you and your factory employees a lot of time and effort and help you solve some critical challenges.