When it was first presented, the concept of lean manufacturing (that was originally developed by Toyota) almost sounded like an oxymoron.
We were so used to thinking of factories loaded with raw material, inventory and parts that the idea of adopting a lean approach seemed close to impossible. Nevertheless many factories during the ‘80s and ‘90s adopted lean methodologies.
But, the development of Industry 4.0 as well as new approaches enable taking lean manufacturing to new levels and to become a reality for forward-thinking manufacturers around the world.
According to a recent survey focused on the Automotive industry, 97% of Production Managers said that lean management would be highly relevant by 2030.
The lean-manufacturing concept is quite simple to comprehend, by becoming efficient and by smartly using every resource and solution available, manufacturers are able to significantly reduce waste and save the time and labor involved in almost any process.
As a result, less resources are being wasted while productivity levels go up.
By using strategies, tools and technologies that continuously improve different steps in the manufacturing process, business results can constantly get better. In today’s competitive landscape, this becomes a necessity.
As discussed below, AI-based technologies become smarter and much more sophisticated over time, hence becoming a main driver of lean manufacturing.
But first, let’s dive slightly deeper and discuss the true meaning of lean manufacturing.
Lean and agile: Best friends, not twins
Lean manufacturers are often agile as well, mainly because they are generally more open to new and radical methodologies. This gets many confused as to the exact difference between the two popular management approaches. Let’s sort things out.
While lean manufacturing focuses on specific principles that make the most out of every employee, machine, and material, agile manufacturing is focused on responding to current conditions in the best way possible. Agile manufacturers focus on dividing the work so that each employee has its own responsibilities and is able to make quick adjustments whenever necessary. These shifts could (and should) include paying attention to the resources being used in the process and the ability to use them more efficiently, but that does not make agile and lean the same thing.
In short, let’s consider agility as the ability to respond fast to changes, while being lean is the ability to do more with less.
The lean challenge
As in theory, the lean concept sounds like an ultimate direction to follow, people tend to rightfully wonder how come not every manufacturer in the world is adopting the lean-manufacturing method.
After all, using resources efficiently while boosting productivity sounds just about right.
Well, the answer probably has to do with the challenges each manufacturer must overcome in order to fully and properly implement lean procedures. Just because it’s wise to optimize every process doesn’t mean it’s easy. Here are some of the steps manufacturers must take in order to move in the lean direction:
1. Prevent waste:
There are many different types of waste that should be taken into account, including material, inventory, labor, time, and more. Manufacturers who wish to go-lean need to refrain from reaching a state of overproduction or over-processing, as well as identify defects in these processes.
2. Focus on value
Lean manufacturers understand the value of production steps on a deeper level and map out the value stream to prevent waste and form a smart flow. This includes an on-demand state of mind in which a product is only manufactured when the market deems it necessary.
3. Continuous improvement
Each of the above steps are ongoing, and the work is never really considered done. Errors are identified and treated, automation is implemented in more areas, data is collected and analyzed, and lessons are learned every step of the way.
Yes, you get it right. Being lean means a general shift in the business spirit.
Industry 4.0 for the aid
A significant part of the continuous improvement in lean-manufacturing is derived from the adoption of innovative technologies that enable better utilization of resources, as well as the measuring and analysis of manufacturers’ productivity levels.
That’s why a methodology that has been around for a few good decades is trending more and more since the Industry 4.0 revolution. While the human factor is incredibly important, we simply wouldn’t be able to reach optimal results without the right tools.
Traditional lean-techniques are still very much relevant. When combined with Industry 4.0 technologies such as AI, big data, and IIoT, they create “lean manufacturing on steroids” that is more equipped to tackle any manufacturing task.
Chances are that we still haven’t seen half of what technology can do for lean manufacturing since each of the technologies involved and the combination of them with lean management methodologies have not reached their full market potential. Far from it, actually.
As AI and IIoT continue to trend alongside lean production methods, we will experience the true power of this revolutionary approach. This depends on companies’ ability to win the challenges we’ve mentioned above, but success is well on its way. Companies that will make a successful transition and will reach new opportunities for excellence and growth, as evident in Boston Consulting Group’s research below:
The potential of lean 4.0-based manufacturing becomes particularly clear as we examine the nature of some of the more prominent technologies in light of traditional lean principles:
- Continuous improvement and AI: Some Artificial Intelligence technologies like machine learning become more sophisticated and effective as time goes by and historical data is added, since it relies on data that is being collected and analyzed over time. This means that factories looking to implement AI with lean manufacturing in mind are set to experience ongoing improvement based on the data that is gathered and put in the right context.
- Focus on value and the digital twin: Industry 4.0 technology also leans on the concept of digital twins, which is a virtual replica of real manufacturing procedures and environments, to simulate many different scenarios and learn which scenario is optimal. This fast testing environment also saves the waste that could have been created by failed attempts.
- Automation and waste prevention: Smart automation technology, which includes IIoT devices, enables smoother operations and communication that save time and error. Fewer employees are involved in each process, which reduces the risk of human error and rework. In addition, physical waste is saved thanks to smart production scheduling, material management, machine predictive maintenance and alike that use industry 4.0 technology, and the list goes on.
The above advantages are translated to better business performance on many levels. Here are a just a few prominent examples:
- ‘Just-in-time’ material management: Accurate predictions mean no extra inventory will be taking up costly space as well as less wasted, expired materials. In the manufacturing world, where materials are particularly expensive, this is big news.
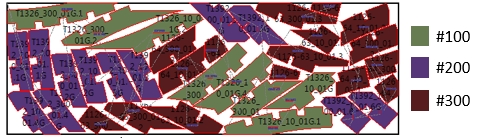
Example: ‘Just in time’ optimization of material cutting: By letting AI prepare your cutting plans you can save raw materials and ensure that you don’t overcut or undercut pieces, but, rather, accurately meet the needed demand for materials.
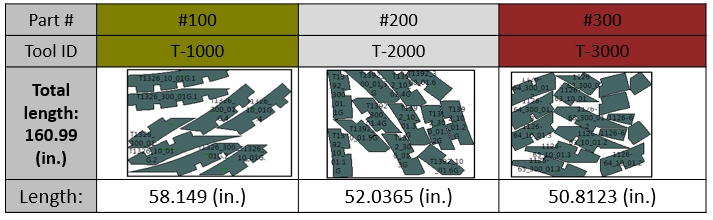
Below a traditional cutting plan:
Alternatively, here, an example of an AI optimized cutting plan. All parts are mixed and cut from the same sheet, resulting in almost 20% material saved:
- OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness) optimization: Industry 4.0 technologies enable manufacturers to maximize the availability levels of their entire machinery, as well as predict or initiate maintenance-related downtime. We’ve recently written about the ROI of Industry 4.0 technologies and explained that among other utilities, it lets manufacturers focus on utilizing their existing machinery instead of purchasing new ones.
And here’s a guide that you can download in order to learn how to estimate the ROI of industry 4.0 technologies:
- Increased productivity: Automation enables workers to use their time wisely and focus on tasks that truly require their expertise. By reducing the tedious tasks that take up a lot of time but do not require complicated thinking, workers both enjoy their work and are able to get a lot more done in less time. The result is an immediate uplift in efficiency and employee retention, which equals business growth.
Summary
These are exciting times for manufacturers, as technology is finally by their side too, and they can leverage tools to supercharge leading methodologies and gradually unlock their full potential. We are only beginning to see what Industry 4.0 solutions can do for lean manufacturers, and following one of the main principles of this approach, we can expect to see continuous improvement and growth in the future.