The term digital twin may seem like something taken straight out of a Sci-Fi novel, but when you learn what it actually means to manufacturers you realize that it is actually not only exciting but quite valuable too.
“Think of a digital replica…”
On a very high level, a digital twin is a digital replica of a physical asset, system, or process. In the context of manufacturing, a digital twin is a virtual model of a manufacturing process, production line, or individual machine that can be used for simulations, analysis, and optimization.
Digital twins can be used for manufacturing optimization, to improve efficiency, reduce downtime, and identify potential issues before they occur. For example, a digital twin of a production line can be used to simulate different scenarios and optimize the production process by identifying bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
Digital twins can also be used to monitor the performance of physical assets in real-time and identify potential issues before they become problems. This can help to reduce maintenance costs and improve the overall reliability of the manufacturing process.
Overall, there are many benefits of digital twins in manufacturing and they are an important tool in the manufacturing industry, as they allow companies to optimize their processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
the digital twin concept in manufacturing represents an environment almost identical to the physical production floor, only fully virtual and digitized. This replica may be created for one particular section within the work environment or the entire plant, and is used to simulate, predict and optimize every part of the manufacturing process.
Modeling isn’t new… only now it’s being leveraged as part of the 4th Industrial Revolution.
The advanced technological enablers and capabilities implemented within a digital twin environment may include IoT, AI, advanced analytics, and others. The digital twin uses machine learning capabilities, for instance, to generate accurate predictions for multiple scenarios which may or may not take place on the production floor; it helps decide between different alternatives based on estimated performance, prepare for multiple worst-case scenarios, and analyze incidents.
Did you know?
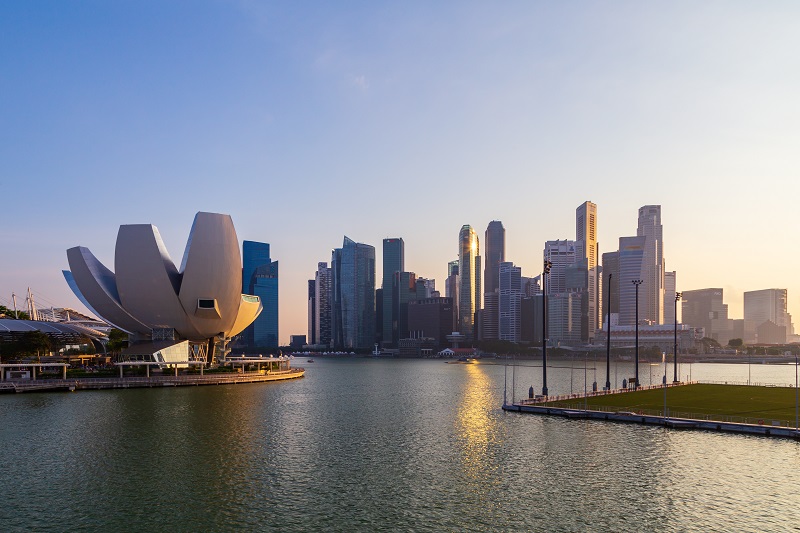
One great example of digital twins usages comes from Singapore, where the city-state itself has a replica to support city planners!
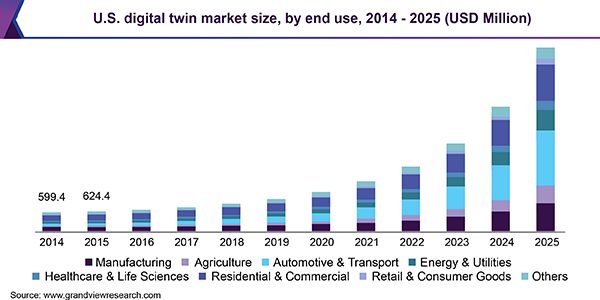
The global digital twin market size was valued at USD 2.26 billion in 2017 and is expected to expand at a CAGR of 38.2% from 2018 to 2025. In addition, according to a recent survey by Gartner, 75% of the organizations that are currently implementing IoT capabilities also use digital twins or plan to do so within a year.
Source: Grand View Research
Digital twins in manufacturing
It’s easier to list the ways in which digital twins may not be used in manufacturing optimization that it is to list all the wonderful possibilities they bring to the table. In fact, I almost can’t seem to come up with any manufacturing scenario in which a digital twin will fail to come in handy.
Industry 4.0 technologies lean on digital twins. By adding sensors to specific assets, collecting data, building digital replicas and using machine based intelligence, manufacturers can understand how these assets will behave in real-time, in the real, physical world. Then, they can make smart decisions with confidence, and boost business results.
Digital twins are used to analyze material-consumption to reduce costs, identify inefficiencies, simulate tool tracking methods and more. Manufacturers create a digital clone for specific equipment items and tools, complete products or systems, entire procedures, or anything else they wish to optimize within their production floor operations.
Sometimes, the digital twin can be the original product and the physical version is created based on digital simulations. Other times, the physical product may already exist but can be replicated and later on customized in many ways using a digital version.
Thanks to the growing implementation of IoT solutions in manufacturing, the next stage of harnessing these connected devices to form a digital twin is easier. The manufacturing market today is relatively educated on the advantages of using such solutions, which helps to pave the way for this smart approach.
Some specific use cases are currently more prominent than others.
We’ve identified 5 main digital-twin advantages that transform the manufacturing world
With many use cases come many advantages, but the following five prove to be more significant to manufacturers:
- Process control and management: Once you have created a digital twin for every asset on the manufacturing floor, it is possible to control and manage complete processes. the representation of a process is called a digital thread, which includes digital representation of every operation, equipment, material and the relevant production history related to these objects. This digital representation enables manufacturers to manage and control every step of the process in a more efficient way and make necessary adjustments while taking all the variables into consideration. Furthermore, it improves visibility and traceability, which are key to auditing and quality processes.
- Visibility: Digital twins enable to capture the location, status and condition of every asset on the factory floor. No matter how big and complex the production environment is or the quantity of the assets you want to track, the digital twin enables manufacturers to gain control of the entire factory, down to the granular level of every station and object.
- Factory management: Digital twins allow manufacturers to enjoy a smart, controlled production chain and enable managers to gain immediate access and overview of the production floor. If anything goes wrong, factory managers can detect the problem, identify the cause and recommend the right solution in real-time.
- “What if” scenarios: An AI-powered software can evaluate enormous amounts of scenarios and recommend on the optimal plan. This is possible by using a digital model of the manufacturing process, comprised of digital twins. Running ‘what if’ scenarios on a daily basis, allows manufacturers to better cope with changes in schedules, unexpected rush orders and responding to production line malfunctions.
- Analysis and predictions: Not only future scenarios are analyzed and prepared for, but also the next possible step manufacturers may take during the process. The machine learning capabilities enable manufacturers to compare performance results for different patterns, analyze every maintenance issue and bottlenecks for multiple possible outcomes, and make an educated move based on data analytics. You can learn about 5 concrete use-cases in this article, which will shed more light on the type of predictions I am discussing here.
Summary
In this article, I examined only a few advantages that the digital twin concept brings to advanced manufacturers, but there is much more to gain from digitizing your factory and fully adopting this concept. This will improve your flexibility and strengthen your competitive advantage. Digital twins might be a virtual replica of your physical assets, but the outcomes and savings are very, very real.