Another year has passed, and here we are again, retrospecting on 2021 and looking forward to the trends and advances that we expect to see in 2022. Especially since the tsunami of uncertainty that’s plagued the aerospace industry since 2020, it’s heartening to know that recovery is expected to kick off this year and to continue over time.
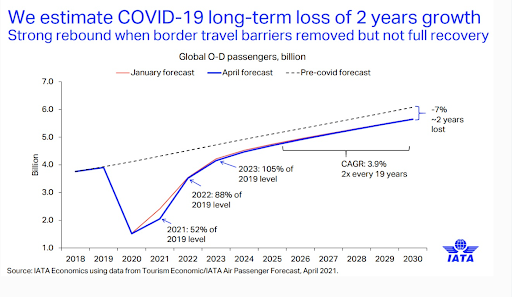
The chart below shows IATA estimation for growth in passengers, year over year.
As you can see from this graph, that doesn’t mean that this is the year we’re going to completely recover from the major hit that the industry took during the pandemic. Still, it’s reassuring to know that experts forecast a strong rebound as more countries open up their borders to international travel.
Technology trends will play a big role in this recovery. In our 2021 trends forecast from last year, we predicted that supply chain optimization, data-empowered real-time decision-making, and workforce optimization would play an ever-larger role in aerospace composites\]o manufacturing. With 2021 now in the rear-view, we can see just how much traction these trends gained and how relevant they are to the core technology that’s being deployed throughout the industry.
However, due to the ongoing pandemic recovery, priorities continue to shift towards compensating losses by cutting costs, boosting efficiency, and implementing technologies that will help us to cope with the next crisis and keep resilience.
Manufacturers are focusing on building future resilience for when demand isn’t stable, supply chains become unreliable, and instant decisions need to be made.
This article will help us gear up for 2022 by focusing on trends that are already rising, around mitigating risks, expanding capabilities, and moving forward into Industry 4.0 and the future of manufacturing.
So, without further ado, what does 2022 hold for aerospace and composites manufacturers?
1. Extreme Automation
Extreme or hyper automation is about pushing automation as close as possible to the hypothetical 100% autonomy of the manufacturing production floor where operators and machines are running fully automated processes. 100% seems impossible, but the industry continuously improves automation towards it, automating more and more functions and processes.
The benefits of extreme automation are clear: From eliminating production delays, streamlining processes to reducing errors and rework due to automation of time-sensitive composite material management. The result is reducing operational costs – a key in the recovery from the pandemic.
As you can see in this article, Forrester discusses the fact that the pandemic’s wake drives Automation trends in general , in order to “gain the ability to reshuffle priorities on a dime by using the latest analytics”.
Extreme or hyper automation is becoming a trend due to the matureness of relevant technologies for manufacturers, mainly the addition of AI layers on top of IIoT automatic data collection capabilities.
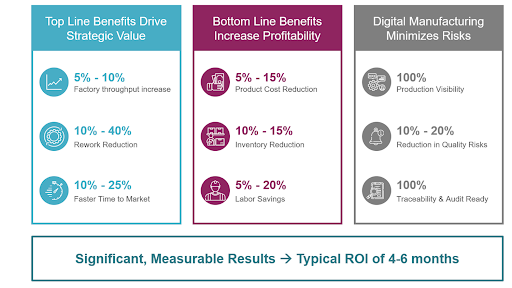
The infographic below shows data coming from Plataine’s customers, and it demonstrates the impact of adding extreme automation on cost reduction and production increase:
As Gartner’s analysts put it, “Hyper Automation enables accelerated growth and business resilience by rapidly identifying, vetting and automating as many processes as possible.”
2. Predictive Analytics and Maintenance
Leave automation aside for a minute, one of the most powerful AI applications for the shop floor is predictive analytics. The most straightforward use case is preventative maintenance.
George J. Newton writes for Business View Magazine, “Ninety-eight percent of businesses report that a single hour of downtime costs them over $100,000. That’s a lot of money to be wasting, which is why adopting preventative maintenance strategies is essential to keep costs down, especially today.”
According to TWJ, “Unplanned downtime costs industrial manufacturers an estimated $50 billion annually. Equipment failure is the cause of 42 percent of this unplanned downtime. Unplanned outages result in excessive maintenance, repair, and equipment replacement”
How strong is this trend? A recent report indicates that “Predictive Maintenance for Manufacturing Industry market is projected to grow with a high CAGR”
Essentially, by analyzing data generated with IIoT sensors and by legacy systems, AI and ML algorithms can predict how likely a machine, a tool, or any piece of equipment will need maintenance or fail, and when. Once the likelihood surpasses a predetermined threshold, the system automatically triggers an alert in real-time and offers concrete recommendations on how to deal with the new situation (e.g. direct the work order to a different workstation, change the shift schedule or alike).
Another use case is predicting the Autoclave utilization rate in each curing cycle for parts that share the same curing recipe, and coordinating (or scheduling) the layup operations and material cutting in accordance (ensuring the Autoclave energy and throughput are maximized, and waste is minimized).
Predictive analytics also has more creative uses. For instance, “critical challenges like demand forecasting require a robust prediction system based on operation data analysis,” writes Gengarajan PV at readwrite. “ Without this, manufacturers can never plan for the future.”
Specific use cases in the Aerospace composites industry:
- Defrosting (thawing) and cutting time-sensitive materials based on accurate demand predictions
- Running scheduling ahead and during the shift to fit the planned production throughput and respond to unpredicted changes
- Coordinating the input to the autoclave to maximize utilization and avoid running them half empty
To learn more, visit this case study:
3.Decision Intelligence
If you want to really help the factory floor manager, don’t flood them with more data, but rather let them know what actions you recommend to take…
Just like a proper GPS navigation system that offers you a new route due to an accident on the highway, rather than just showing lots of data. That’s the difference between ‘data presented in reports/dashboards’ and ‘decision intelligence’ (what I call a true digital assistant).
Along similar lines to predictions, decision intelligence (DI) is built on historical learning and pattern identification. These analytics supplant the impulsive and biased decisions that people make as a painful result of our limitations as human beings.
Gartner predicts “that in the next two years, a third of large organizations will be using decision intelligence for structured decision-making, to improve competitive advantage.”
The biggest challenge, however, is not in collecting or storing data. Rather, it’s analyzing contextual data and turning it into meaningful insights that improve business operations. That’s the role of AI.
In today’s hectic manufacturing landscape that’s full of unpredictable environmental changes, making optimal decisions is becoming too difficult for the human mind without technological assistance. This is especially true when decisions need to be made in an instant and at scale. As part of the pandemic lessons learned, the industry is expected to deepen investments in solutions that offer intelligence layers on top of analytical ones.
To learn more, take a look at our complete guide for turning data into decisions:
In 2022 The Aerospace manufacturing industry will continue to increase its investment in software that adds such capabilities on top of their existing MES or ERP systems. Such solutions use IIoT and AI to reach 100% traceability and visibility , automate composite material cutting plans decisions, scheduling decisions, inventory management decisions and more. Automated alerts and recommendations will be essential to help production managers deal with the amount of data that should be considered as part of the decision making processes.
4. Smart Workforce Utilization
The pandemic taught us many lessons. Between quarantines, canceled business travel, and the massive migration to working remotely, we learned that remote work forces can be quite effective in many cases.
Trends in smart workforce utilization involve Hyper Automation, as it releases the workforce from everything that can be done by technology, in addition to using tech to help experts remotely guide production floor employees. It’s also about gaining visibility and traceability without being physically on premises.
A new Google cloud research reveals – “According to our data—which polled more than 1,000 senior manufacturing executives across seven countries—76% have turned to digital enablers and disruptive technologies due to the pandemic such as data and analytics, cloud, and artificial intelligence (AI). And 66% of manufacturers who use AI in their day-to-day operations report that their reliance on AI is increasing.”
See in this graph what are the top 3 reasons manufacturers use AI in day-to-day operations:
5. Factory Floor Visibility and 100% Traceability
Manufacturing aerospace composites poses unique challenges. Starting with regulations that ensure the highest level of safety, and the highest quality standards. Since many materials are time-sensitive, we need to track and manage them as they move on the factory floor from one station to another, from receiving to the freezer to the autoclave and beyond.
Additionally, it’s crucial to know how much inventory we have on hand and to forecast demand to see if we need to order more materials or if we’re going to be left with ones that are going to expire.
Manufacturers that track time-sensitive material the old-fashioned way (using paper or Excel), miss out on real-time visibility. The result is materials losses, quality defects and rework.
That’s why the industry is moving towards using sensors in an IIoT network alongside AI to accurately monitor inventory and make granular calculations. Traceability and visibility are essential to reduce operational costs and increase quality.
6. 3D Printing
Also known as additive manufacturing (AM), this trend isn’t new and it continues as technology is already having a big impact on the aerospace manufacturing industry, and makes production in some occasions faster, easier, and more cost-effective.
Summary
Without a doubt, 2022 will bring its own set of challenges on top of the existing ones.
However, as it currently looks we have good reason to be hopeful.
To keep up with competition and to quickly recover from 2020 and 2021 losses, manufacturers will have to onboard tech that can significantly improve their production efficiency, cut operational costs, enable extreme automation, and better utilize both inventory and workforce. This will ensure coming out from this unbelievable crisis much stronger than before.
It will be interesting to see what 2022 brings in terms of demand and innovation. While we cannot accurately predict the future, we can see what way the winds are blowing and adjust our sails accordingly.